The choice between direct injection and port injection can be difficult for those looking to optimize the performance and efficiency of their engines.
Both direct injection (DI) and port injection (PI) have their advantages and disadvantages, and it’s difficult to say which one is definitively “better” as it largely depends on the specific application and use case.
Direct injection involves spraying fuel directly into the combustion chamber, whereas port injection injects fuel into the engine’s intake ports.
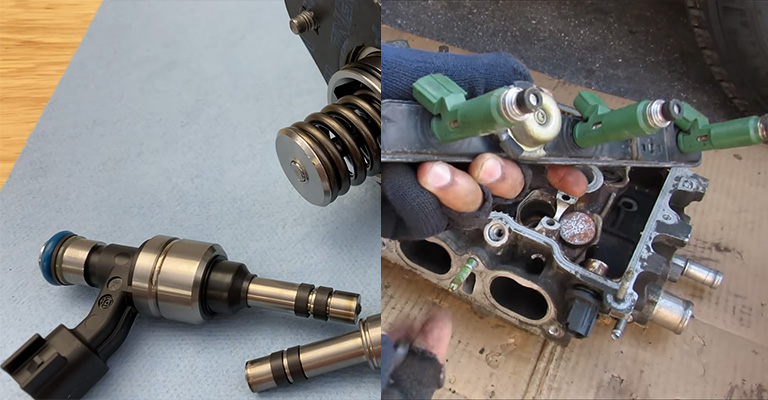

What You Need to Know About Direct Injection Vs. Port Injection
Direct injection and port injection are typically used in gas-consuming cars. When fuel is delivered directly to a cylinder’s combustion chamber rather than through the intake runner, it is known as direct injection.
Fuel injection systems are used in every fuel-consuming car bought in the United States to let diesel or gasoline into the engine’s cylinders to burn it.
In spite of the fact that fuel injection systems are an essential and necessary component of the engine of your car, fuel injection technology affects the fuel efficiency, engine performance, and maintenance costs of the engine.
What Is Direct Injection?
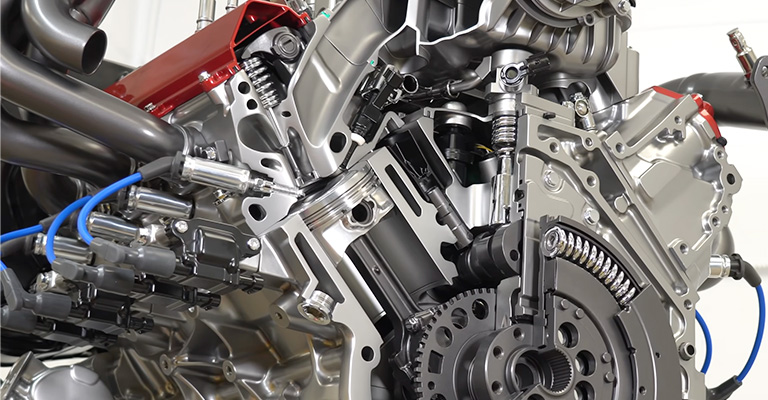
By injecting gasoline or diesel directly into the engine cylinder, it is combined with oxygen, which burns it for energy.
In general, direct injection systems are more fuel-efficient since one less step is required to get fuel to the engine’s cylinders.
What Cars Use Direct Injection?
Fuel efficiency and efficiency have always been significant advantages of direct injection fuel systems, but European car companies have seized upon these benefits to produce more fuel-efficient vehicles.
Moreover, American and Japanese automakers recently reaped the benefits of direct injection fuel systems. The following are some automakers that utilize direct-injection fuel systems:
- Ford
- General Motors (GM)
- Audi
- BMW
- Hyundai
- Kia
- Mazda
- Mitsubishi
- Mercedes-Benz
- Nissan
- Lexus
- Saab
- Subaru
- Volkswagen
What Is Port Injection?
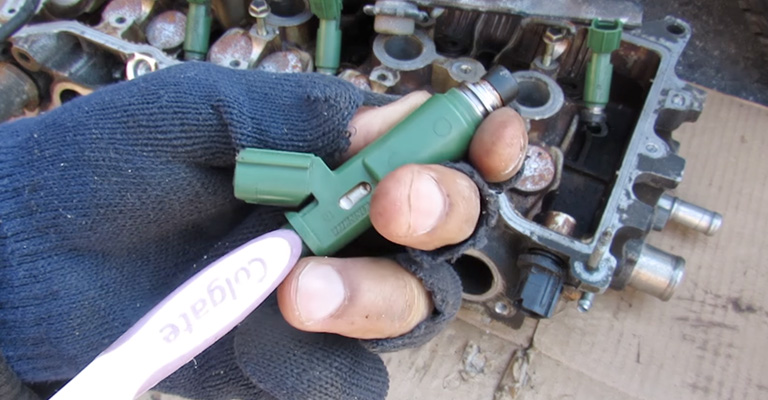

In contrast to direct injection, a port injection fuel system premixes gasoline and oxygen outside of the engine cylinders.
Once the mixture is pulled into the cylinders for combustion, fuel will be produced. Although less fuel-efficient than a direct injection, it is still more fuel-efficient than a carburetor.
What Cars Use Port Injection?
Gasoline cars were injected by port until the turn of the century when it became the default fuel injection system.
There are few car companies that still use port injection in their fuel systems, even though it is not easy to locate new cars that use only port injection:
- Toyota
- Lexus
- Ford
- Audi
Direct Vs. Port Injection: Which Is Better?
Direct injection uses high-pressure fuel injectors that atomize the fuel into smaller particles, creating a more efficient burn and improving fuel economy by 10 – 15%.
The port injection uses low-pressure fuel injectors that rely on heat from the valves to atomize the fuel, which results in better air-fuel mixing and more stable combustion at low RPM.
Direct injection also cools the air inside the cylinder, reducing the risk of knock and allowing more boost and advanced timing at high RPM.
Direct injection is better suited for the wide-open throttle to help reduce engine knock and provide more horsepower.
Port injection is used under low loads to help use less gasoline.
Carbon buildup occurs when carbon deposits accumulate on the intake valves over time. These deposits can lead to decreased engine performance, reduced fuel efficiency, and other potential issues.
Direct injection engines are more prone to this problem than port injection engines.
The advantage of port injection over direct injection in terms of carbon buildup prevention lies in the fuel’s cleaning effect on the intake valves. When fuel is sprayed in the intake ports, it washes over the valves, effectively cleaning them to some extent.
This continuous cleansing action helps inhibit carbon deposits from forming on the valves, promoting smoother engine operation.
Advantages of Direct Injection

- The use of more precise fuel delivery leads to more efficient combustion and better fuel economy.
- The ability to better control combustion timing, leading to more efficient combustion and reduced emissions.
- Power and torque can be increased by utilizing higher compression ratios.
- This type of intake valve is less susceptible to carbon buildup.
Disadvantages of Direct Injection
- Costs and complexity are higher due to higher system complexity.
- Fuel system components can be damaged more quickly if the fuel pressure is high.
- The intake air stream doesn’t carry enough fuel to cool the combustion chamber, leading to engine knocking and detonation.
Advantages of Port Injection
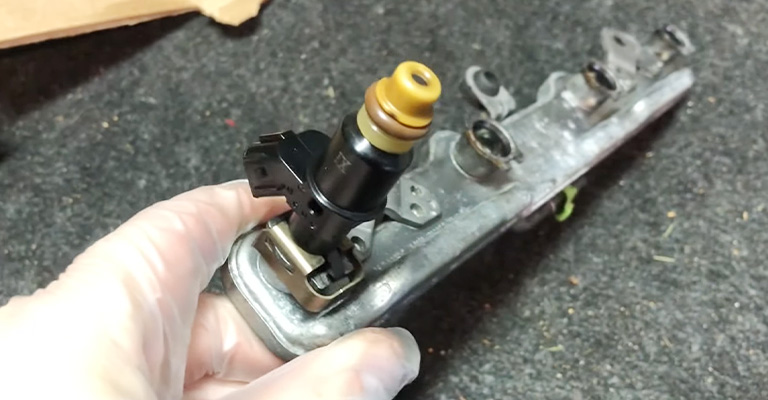

- It is simpler and more reliable than the previous system.
- In comparison with direct injection, the cost is lower.
- The presence of fuel in the intake air stream can help reduce knocks by cooling the combustion chamber.
Disadvantages of Port Injection
- The fuel is delivered less precisely, causing less efficient combustion and, ultimately, worse fuel efficiency.
- Combustion timing is less controlled, resulting in performance and emission control limits.
- As time passes, more carbon accumulates on the intake valves.
Dual Fuel Injection
With the dual fuel injection system, car manufacturers have combined port and direct injection into one setup to overcome both systems’ drawbacks.
Interestingly, combining these two systems increases their advantages while eliminating their drawbacks.
The only drawback of this system is the increased number of moving parts and the increased cost of production.
How Does A Dual Fuel Injector Work?
When running at low RPMs, the system will primarily use a port fuel injector for an improved air-fuel mixture. Port fuel injection will give the engine all the benefits of port fuel injection.
Upon increasing RPM, however, the direct injector continues to function, and the port injector stops. Direct injection improves combustion efficiency by operating faster at higher RPM, enhancing performance.
Port injectors will provide enough fuel at high speeds when the direct port injector cannot anymore provide the fuel as the RPM increase. Both injectors will work at high RPMs for fuel delivery while simultaneously supplying fuel to the cylinder.
Conclusion
Both direct injection systems and port systems have advantages and disadvantages; a dual injection system combines them both.
Essentially, a dual injection system combines the advantages of both injection systems while at the same time eliminating their disadvantages.
Therefore, more and more automakers are installing dual fuel injection systems in their new engines.





Any one with Automotive experience will tell you that you have it backwards as far as carbon build up on intake valves. Port injection prevents carbon buildup on intake valves because the air/fuel mixture precedes the intake valves there by cleaning the valves as air fuel mixture passes over the valves. Direct injectors spray fuel directly into the cylinders, the intake valves receive no cleaning effects of fuel. This is why wise folks will put an oil catch can on a direct injected engine!