A vehicle’s power comes from the combustion of air and fuel, which takes place inside its cylinders. To accelerate and spin its wheels, a vehicle generates power in this way.
During gasoline combustion, power is produced inside a cylinder chamber, and your vehicle moves as a result. The most common engine has four, six, or eight cylinders, where more cylinders mean more power.
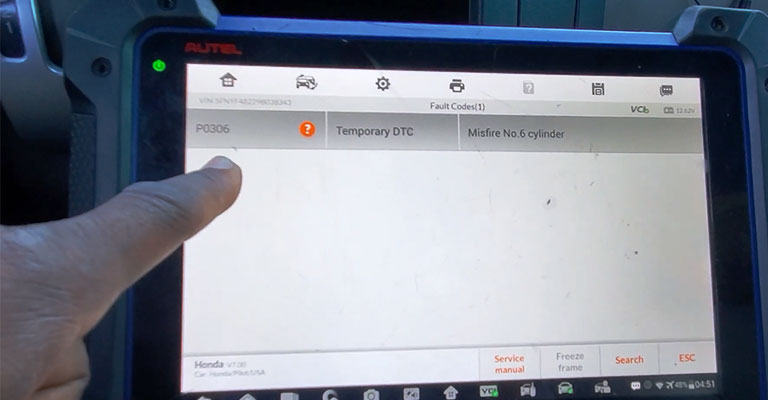
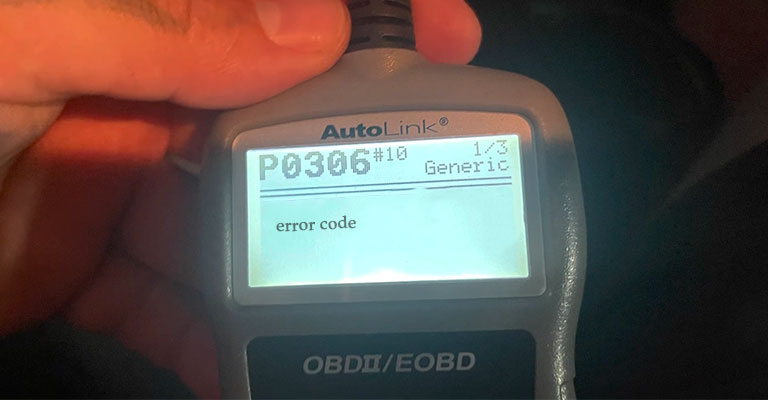
Fuel is ignited at very specific times to generate power by moving pistons. In most cases, misfires are caused by improper timing of the ignition. An error code P0306 indicates cylinder #6 is experiencing misfires.
Multiple misfires can occur for various reasons, including faulty spark plugs or low engine compression. In addition, ignition failure, catalytic converter damage, and dangerous conditions can occur when this code is not fixed immediately (the same day, if possible).
P0306 Honda Meaning
According to the power needs of a vehicle, there are usually between 4 and 8 engine cylinders. In case of a misfire, the car’s computer will send a code indicating which cylinder is malfunctioning.
When a cylinder misfires, some power can still be generated, but not enough to meet the driver’s acceleration demands. ECM (engine control module) code P0306 is produced when the ECM detects a misfire in cylinder number 6 of the engine.
The misfire in cylinder number 6 is caused by an air/fuel mixture that cannot ignite. Due to this, the crankshaft position sensor signal varies as the engine’s speed fluctuates. As a result, the ECM reports a misfire in the specific cylinder.
P0306 Honda Code: What Causes It?
There are many reasons why a vehicle may misfire, including a faulty ignition system, a malfunctioning fuel system, or an internal engine issue.
A worn-out or damaged spark plug coil pack is the most common cause, especially if you haven’t had your car tuned up in a while. These are some of the most common causes of the error code P0306.
- Fuel Injectors That Are Clogged, Dirty, Or Damaged
Misfires can be caused by insufficient fuel in the cylinder. A faulty fuel injector causes low pressure in the cylinders.

- A Low Compression Ratio
In some cases, misfires can be caused by low compression in the cylinder caused by defective valves or rings.

- The Valve Cover Is Leaking
There is a possibility that cylinder number 6 could be shorted if oil leaks into the spark plug holes on the valve cover.
- The Spark Plug Wire Is Worn Out Or Damaged
Cylinder number 6 may stop firing if a spark plugs boot or spark plug leaks ignition spark to the ground.
- The Ignition Coil Is Faulty
Cylinder number 6 may stop firing if there is a crack in the insulation or an open circuit in the ignition coil.

- Spark Plug With A Fault
An insulation crack or fouling may prevent the bad spark plug from properly firing in cylinder 6.
- There Is A Leak In The Spark Plug Wire Or Plug Boot
In cylinder number 6, the ignition spark is leaking to the ground from the spark plug wire or plug boot.
Symptoms Of The P0306 Code
In general, a P0306 error code will be accompanied by the following signs:
- This error code is often found with other error codes such as P0300, P0301, P0302, P0303, P0304, P0305, P0307, and P0308.
- There is an odd odor coming from the engine’s exhaust
- Fuel economy may decline, exhaust smells like fuel, engines idling rough or lack power in some cases
- When accelerating, the engine runs rough, hesitates, or jerks
- There is a flashing or ongoing check engine light
- It is possible for drivers not to notice adverse driving conditions

Diagnosing Error Code P0306
If there is any damage to the connectors or wiring harness, begin by inspecting them. All error codes and freeze frame data should be recorded using an OBD2 scanner. Next, visually inspect the fuel injector, ignition coils, and related wiring using the above information.
Make sure the wiring is not damaged or loose. Next, check if the ignition coil is the problem by removing it and swapping it with another cylinder. Once the engine, and ETC codes have been cleared, do a road test to determine whether the problem persists.
Visually inspect the spark plug. Any signs of damage or fouling should be checked and replaced if necessary. Try swapping the spark plug to another cylinder to see if the misfire persists. Alternatively, if there is no problem with the ignition system, check for vacuum leaks connected to the number 6 cylinder.
Fixing Code P0306
To figure out what is causing the misfire fault, it’s first important to get it diagnosed. A Honda-certified shop can pinpoint the problem and provide an accurate repair estimate if your vehicle is misfiring, and you don’t feel comfortable diagnosing it yourself.
As well as figuring out what’s wrong before you spend time and money on the wrong parts, these shops can help you save time and money.

Most Common P0306 Fixes
Examine and test the ignition system around the cylinder to determine whether you need to replace coil packs, plugs, or wires. Unfortunately, these three things are usually the culprits most of the time.
Replace the coil pack, wire, and plug of Cylinder 6 with another cylinder to reset the trouble codes. The change in these three components will result in a different P030X code since by moving those components, the trouble code will register in a different cylinder.
Replacing or testing them after that is a good idea. Using this method, you can determine if your ignition components need to be replaced easily and cheaply.
What Is The Cost Of Fixing Code P0306?
An engine with P0306 can have many causes, including old spark plugs, vacuum leaks, and poor compression. An accurate estimate can only be given after thoroughly diagnosing the problem.
In most shops, diagnosing your car begins with an hour of diagnosing time. After that, it typically costs $75-150 based on the shop’s labor rate.
The diagnosis fee is usually applied to any repairs the shop requires if the shop performs the work. After you have the P0306 code, a shop can estimate how much it will cost to fix your car.
To resolve the underlying issue behind P0306, one or more of the following repairs may be required. Parts and labor are included in these prices, which are based on national averages. Your costs may vary depending on where you live and what type of vehicle you have.
- The cost of a fuel pressure regulator ranges from $200 to $400
- The cost of a fuel pump ranges from $1300 to $1700
- The cost of a vacuum leak is between $100 and $200
- The cost of fuel injectors ranges from $1500-$1900
- The cost of spark plug wires ranges from 180 to 240 dollars
- The cost of ignition coils varies from $230 to 640 (in some cases, you will have to remove the intake manifold)
- The cost of spark plugs ranges from $66 to $250
Is Code P0306 A Serious Error?
It is dangerous to drive a car with a misfiring cylinder. In the event of a misfire in cylinder number 6, an overly rich engine can damage the catalyst. In addition, it affects how your engine runs, makes it hesitate when accelerating, and increases fuel consumption.

In this case, DTC P0306 is something that must be addressed immediately and should not be ignored. It is quite costly to repair a misfiring cylinder than to replace a catalytic converter if you disregard this code.
Final Words
A high priority should be given to fixing P0306. In contrast to many other OBDII codes, this one is directly related to engine combustion.
It indicates that cylinder number 6 isn’t contributing to engine power when the crankshaft sensor doesn’t receive an acceleration from the crankshaft.
Misfiring cylinders can damage the catalyst and cause the engine to run excessively rich. In addition to running rough, the engine will hesitate while accelerating due to the misfire. Again, this is a serious problem and should be addressed as soon as possible.