Drivers can detect potential issues in their vehicles with the help of trouble codes. It can seem intimidating to deal with trouble codes. In this brief guide, you can learn more about the definition, common causes, and symptoms of the P2185 code on your scan tool.
It means “Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor 2 Circuit High” in diagnostic trouble code (DTC) P2185. Engine coolant temperature (ECT) circuit electrical faults are detected by the powertrain control module (PCM), and this code is set.
An engine’s ECT sensor measures the coolant’s temperature through a thermistor. In most cases, it’s found within the coolant passage of the cylinder head. A low coolant temperature causes this sensor to have a high resistance, while a high coolant temperature causes a low resistance.
The PCM monitors ECT sensor voltage changes to determine the temperature of the coolant. Whenever the ECT indicates a temperature below what is expected after more than a few minutes of running, the PCM sets the P2185 fault code. The PCM can also set this code if the ECT sensor’s resistance differs from expected.
What Does Engine Code P2185 Mean?
The P2185 diagnostic trouble code refers to the “Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor 2 Circuit High”. You need to have a mechanic diagnose the specific cause of this code triggering in your case. It may be triggered for a variety of reasons.
A code of this type indicates that the sensor reports a cooler coolant temperature than what may exist in the PCM (Powertrain Control Module).
What Are The Symptoms Of The P2185 Code?
The only symptom commonly observed is a Check Engine Light. A PCM that concludes that the vehicle is operating at a temperature it is not might result in a very rich or lean air-fuel mixture because it does not have an accurate voltage reading.
What Causes The P2185 Code?
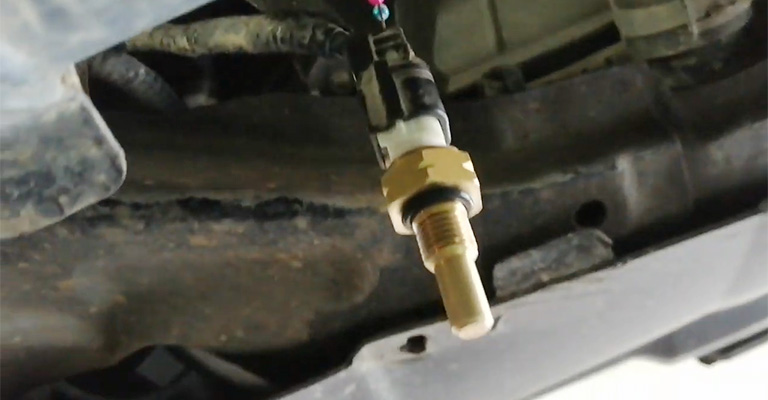

A PCM monitors the engine’s operating temperature with two sensors, including the ECT (Engine Coolant Temperature). Using sensor 1 and sensor 2, as well as the motor’s run time, PCM compares voltage readings.
After operating the motor for a long time, the PCM will determine which sensor is reading incorrectly based on the coolant temperature, which should be warmer than the ambient temperature.
How Does A Mechanic Diagnose The P2185 Code?
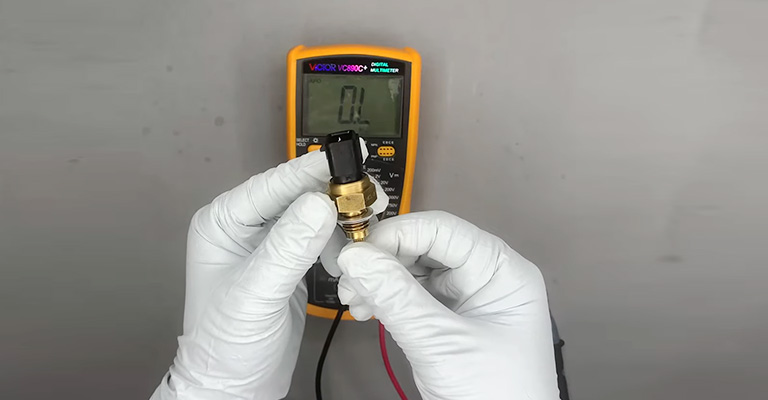

When you connect a scan tool and read the scan tool data, you can usually diagnose the problem quickly. It is simple for the technician to compare sensor 2’s temperature reading with what he or she knows to be true.
In addition to showing how much the car is cold, the sensor should also show how much it is hot. There may be instances where the sensor is simply out of specification when compared to what the PCM expects.
In this case, a technician must remove the sensor from the unit and bench-test it. A multimeter with an ohms setting and something to heat up the sensor are required for bench testing this type of sensor.
You can usually get the job done with a small butane torch. We can measure the sensor resistance using a multimeter, whereas a torch is used to gently warm the sensor.
Warming the sensor should result in a proportionate change in resistance. Manufacturers will have different curves for temperature and resistance depending on the sensor. You will receive this information from the manufacturer.
Common Mistakes When Diagnosing The P2185 Code

Often, we forget to check the coolant level. Low coolant levels can cause many unpredictable symptoms and codes. A good diagnosis can only be made if the coolant level is full and the thermostat is functioning properly.
Your cooling system keeps your engine from overheating. If there are two sensors, it can be challenging to identify which is sensor 1 and which is sensor 2. It is common for us to replace the wrong sensor at times.
Determining which sensor is sensor 1 may not always be as straightforward as it seems. It is better to get information from some manufacturers than from others. If a mechanic is unsure which sensor is which, it may be prudent to replace both, depending on the cost and difficulty of replacing them.
Sensors usually have problems with wiring or connectors, not the sensors themselves. It is important to inspect the connector and the harness that is connected to it. If the sensor bench test is good, the harness to the PCM may need to be checked for continuity (a high-resistance wire may be required).
What Repairs Can Fix The P2185 Code?
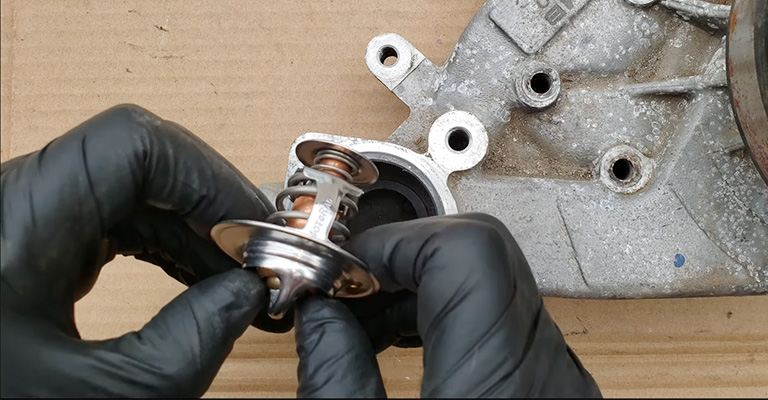

- Replacement of a thermostat
- Leaks in the cooling system need to be repaired and filled
- Connectors and harnesses for ECT
- The ECT sensor can be updated
It is a complex process to fix DTCs. There are several causes of different codes, and each cause has a different solution. The vehicle manufacturer also recommends using their own repair procedures.
It is impossible to fix the P2185 code in a Honda with the same solution that fixes the code in a Volkswagen. The fix for DTCs isn’t as simple as it seems.
A DTC can only be diagnosed and fixed with special tools and expertise. To avoid costly repairs down the road, you should leave DTC repair to a certified mechanic if you’re not confident in your skills.
How Serious Is The P2185 Code?
Usually, this code is not a problem, as manufacturers will only use this code if they use two or more ECT sensors. As a result of redundancy, the manufacturer can calculate the air-fuel mixture under varying conditions and replace one sensor if it fails.
As a result, the PCM will use the coolant temperature sensor as the primary sensor when deciding which mode to use. In either case, the air-fuel mixture needs to be tuned, regardless of whether it is cold when starting up.
There is a possibility that the vehicle will not start if the sensor this code represents fails, depending on the programming the manufacturer uses. Once you do manage to get it going, the tailpipe will emit black smoke with excessive richness.
Can I Drive With P2185 Code?
This sensor generally does not display the engine temperature on the dashboard, so it can cause the engine to overheat fatally when this code is present.
By translating, this means that an engine can overheat if the radiator fans are not functioning properly. The dashboard may show a normal temperature reading, despite the engine temperature being indicated.
It is important to remember that, in most cases of engine overheating, the damage has already been done by the time the temperature gauge indicates an abnormally high reading, so all warning lights related to the cooling system must be taken very seriously.
Other Notes About P2185
There are no differences between the P2185 and the P0118. These two codes are only distinguished by the fact that OBD-II code P2185 refers to the #2 ECT sensor circuit. As a result, cars with P2185 codes have two ECT sensors.
The correct sensor circuit must be diagnosed and repaired when dealing with the P2185. You can view DTCs that are currently registered on your vehicle when you plug your OBD-II scanner into the vehicle’s OBD-II port.
P2185 and other related codes mean that you should immediately stop driving your vehicle and take it to an auto repair shop for diagnostics and repairs.
Final Words
There is a possibility that the P2185 code could render the vehicle undrivable, though in most cases, it will only result in the Check Engine Light coming on. The results will differ according to the manufacturer’s choice of programming and the exact nature of the sensor failure.
When a sensor fails completely, drivability symptoms often appear, but typically it’s because the sensor’s response isn’t as accurate as the computer expects. It is often necessary for the manufacturer to reflash the PROM (Program Read Only Memory) in the PCM as a result of this.




