The air-to-fuel ratio significantly impacts your engine’s performance since it determines how effectively an internal combustion engine performs.
So, running an engine with a lean air-fuel (LAF) ratio often proves advantageous, offering higher fuel efficiency, lower emissions, and enhanced performance.
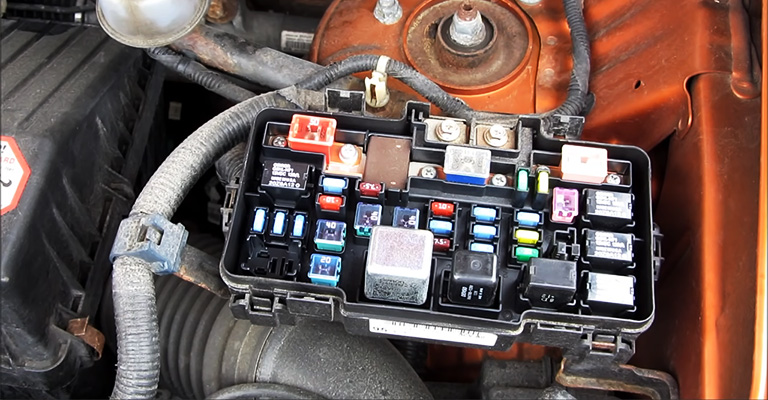
Now, the question that arises here is, “What does LAF mean on a fuse box?”
Generally, a fuse that safeguards the air-fuel ratio sensor is called LAF on a fuse box in most automobiles.
However, understanding how an automobile engine functions are necessary to comprehend LAF.
How a Car Engine Works?
The car engine is the heart of the car and gives it the necessary power and efficiency. It operates in a highly disciplined and sophisticated manner. Car engines can be of various types, such as gasoline, diesel, or electric.
The gasoline engine is the most popular in most of our passenger vehicles. Your engine may be driven by gasoline, diesel, or electricity but follows a similar principle.
The engine runs your vehicle by transforming fuel and air into mechanical energy. This process is known as combustion, where your car engine mixes air and fuel and ignites to create a controlled explosion. It will power your pistons attached to it and creates a rotational motion.
After that, the crankshaft converts this up-and-down motion of the pistons into rotational energy that powers the wheels.
Understanding Air-to-Fuel Ratio in Car Engine

As mentioned, the air-to-fuel ratio is a crucial factor in determining the combustion reaction by air and fuel required for an engine to power a vehicle. It refers to the proportion of air and fuel utilized in the combustion process.
As an internal combustion engine needs a mixture of fuel and air to produce power, the air-to-fuel ratio significantly determines how effectively the engine performs.
- Stoichiometric ratio – A mixture that possesses the ideal proportion of air to fuel for full combustion is called a stoichiometric ratio.
This mixture is the most effective for generating power and is utilized in most internal combustion engines. The stoichiometric ratio is around 14.7:1 for gasoline engines and around 14.5:1 for diesel engines.
- Rich air-fuel mixture – When a mixture has more fuel than air, it is referred to be a rich mixture. Engines that demand more power, like racing engines, use a rich air-fuel mixture.
- Lean air-fuel mixture – A mixture with more air than fuel is called a lean mixture. This mixture is used with engines built for excellent fuel efficiency, such as those seen in some hybrid cars.
There is a trouble code showing on Honda PCM due to the high air-fuel ratio, the code is called – P219A Honda
Influence of Air-to-Fuel Ratio on the Performance of an Engine

An engine’s performance can be impacted by several factors, including the quality of the fuel used, the engine’s construction, and the shape and dimensions of the combustion chamber.
In addition, the air-to-fuel ratio in an engine is a notably important component that plays a vital role in determining how well the engine performs because the mixture is required for complete combustion to occur.
As mentioned earlier, the air-to-fuel ratio can be of three types. Every sort of mixture possesses unique qualities that can significantly impact how well and efficiently an engine operates. The following list contrasts and compares the three forms of air-fuel mixtures.
- Stoichiometric air-fuel mixture
- Has the appropriate fuel-to-air ratio for complete combustion.
- It is a common internal combustion engine fuel.
- Offers the most effective blend for generating power.
- Produces little pollution and reduces emissions.
- Rich air-fuel mixture
- Has a larger fuel content than air.
- Generally, the air-fuel ratio is less than the stoichiometric ratio.
- Used in motors that need extra power, such as racing motors.
- Increases power production compared to lean and stoichiometric mixes but decreases fuel efficiency.
- Increases emissions and releases significant amounts of pollution.
- Lean air-fuel mixture
- Has more air than fuel by volume.
- Typically, the air-fuel ratio exceeds the stoichiometric ratio.
- Utilized in high-fuel-efficiency engines.
- Decreases fuel consumption but may increase engine temperature, resulting in engine damage.
- Less power is produced compared to stoichiometric and rich mixtures.
Now we have a basic understanding of the operation mechanism of a car engine and how a proper air-to-fuel ratio is required for optimum performance. In modern cars, based on the demands of the car at a particular time, a LAF (air-fuel ratio) sensor is installed on a fuse box to monitor and control the amount of air and fuel supplied to the engine.
LAF on a Fuse box

The term “LAF” on a fuse box often refers to a fuse that safeguards the air-fuel ratio sensor. It’s a vital feature of the engine control system that monitors the air-fuel mixture and aids in adjusting it to ensure optimal performance and fuel efficiency.
Moreover, the LAF sensor is typically found near the car’s engine, in the exhaust system. It comprises a heating element that enables the sensor to quickly attain operational temperature and a sensing device exposed to exhaust gas.
A unique coating on a ceramic substance is the sensor element, which responds to oxygen in the exhaust gas.
How Does a LAF on a Fuse Box Work?
The LAF sensor generates a voltage signal that changes in response to the amount of oxygen in the exhaust stream.
So, the engine control module receives the voltage signal and, with the help of this data, adjusts the air-fuel ratio to keep it at the correct level.
Your LAF sensor compares the oxygen content in the exhaust gas to that in the atmosphere. Based on this comparison, the sensor determines whether the air-fuel combination is too rich or too lean.
The LAF sensor will generate a low-voltage signal if there is a rich air-fuel mixture, meaning there is more fuel than oxygen or vice versa.
This means it will generate a high-voltage signal when your mixture gets lean or when there is more oxygen than fuel. The engine control module uses this signal to modify the air-fuel mixture to maintain the required ratio.
Final Words
After reviewing this article, you should know the LAF’s meaning on your fuse box. But before knowing how the LAF mechanism works, you must understand how your engine works.
This way, you’ll better grip the LAF working process. However, if you face any issues with this sensor, the best possible solution will be to consult an expert.




