A car’s OBD-II code is useful for finding out what’s wrong with it. It is possible that one of the oxygen sensors in your vehicle is malfunctioning if your scan tool displays a P0137 trouble code.
An automobile’s powertrain computer or PCM triggers code P0137 when it detects an extended period of low oxygen sensor voltage.
It is also possible that the air-fuel ratio sensor was left in a lean-biased mode for too long (depending on the make and model of your vehicle. Let’s explore what a P0137 means, its causes, and how to fix it.
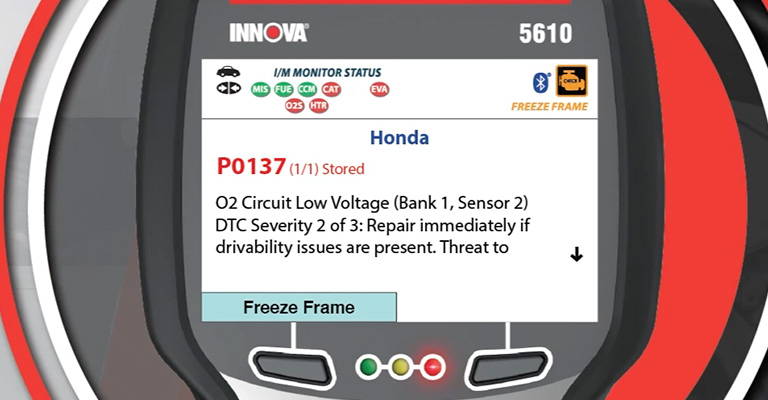
P0137 definition: O2 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 1, Sensor 2)
In the exhaust system after the catalytic converter, oxygen sensor 2 is located downstream. A catalytic converter is measured for proper operation by measuring the ratio of air to fuel that comes out of it.
A constant air/fuel mixture adjustment is made by the powertrain control module based on input from the oxygen sensors.
If the catalytic converter is working correctly and the air/fuel ratio of the engine is correct, the downstream oxygen sensor (sensor 2) should produce a steady voltage of approximately 0.1-.95 volts.
An oxygen sensor downstream is experiencing low voltage (roughly 450 millivolts or less) for more than 20 seconds when trouble code P0137 is set.
The Most Common Problems That Trigger The P0137 Error Code

- There is a need to update PCM software
- The PCM is defective
- The temperature sensor for the engine coolant is defective
- There is a problem with the wiring or circuit of the sensor
- Leaks in the intake air system (including vacuum leaks)
- Fuel pressure is low
- Leak in the exhaust system
- Catalytic converter with a defect
- Oxygen Sensor/Air Fuel Ratio Sensor Defect
- Oxygen Sensor/Air Fuel Ratio Sensor Heater Circuit Failure
What Are The Symptoms Of The P0137 Code?
- The O2 sensor in question may be leaking exhaust before or near it.
- You will see the Check Engine Light illuminated.
- It is normal for the engine to run rich while the sensor is being tested.
What Are The Steps A Mechanic Takes To Diagnose The P0137 Code?

- Verifies failure by scanning codes and documenting freeze frame data.
- Analyzes data from the O2 sensor to determine if the voltage switches rapidly between low and high.
- Conduct a corrosion check on the O2 sensor wiring and harness connections.
- Ensure that there is no physical damage or fluid contamination on the O2 sensor.
- Before the sensor is installed, it checks for exhaust leaks.
- Performs specific pinpoint tests as prescribed by the manufacturer.
What Are The Common Mistakes When Diagnosing P0137?
Here are some easy tips to prevent misdiagnosis:
- To prevent low voltage readings caused by excess oxygen getting into the exhaust stream, fix any exhaust leaks before the sensor.
- Ensure there are no contaminants in the O2 sensor, such as oil or coolant.
- Ensure that any damaged harness is repaired properly so that sensors will not exhibit erratic readings.
- Replace the catalyst if it has come apart if the O2 sensor was damaged by a broken catalyst.
How Serious Is The P0137 Code?

If any O2 sensor malfunctions, the ECM cannot correctly control the fuel-to-air ratio of the engine’s fuel mixture. Some engine components may be prematurely damaged due to this, leading to poor fuel mileage.
It is possible that exhaust leaks can cause the O2 sensors to give low output voltages as a result of low output voltage from the O2 sensor.
How Much Does It Cost to Fix Code P0137?
Any number of problems can cause P0137, from a failed O2 sensor to faulty wiring to exhaust leaks. The best estimate can only be provided after the issue has been properly diagnosed.
Most shops will start your diagnostic time with an hour of labor (time spent diagnosing your specific issue) if you take your car to them for diagnosis. In general, this cost is between $75 and $150, depending on the shop’s labor rate.
When you have any required repairs performed by the shop, the diagnosis fee will typically be applied. In this case, you’ll need to consult a shop for an accurate estimate of repairs to fix the P0137 error code.
The underlying issue behind error code P0137 may require one or more of the following repairs. A repair estimate includes the costs of relevant parts and labor involved in making the repair for each possible repair.
- $100-$200 for vacuum leaks
- The cost of a fuel pressure regulator ranges from $200 to $400
- $1300-$1700 for fuel pumps
- Repairing an exhaust cost $100-$200 (if it needs to be welded)
- The cost of an oxygen sensor ranges from $200 to $300
Can I Drive With The Code P0137?
Trouble code P0137 can be tolerated for a short period of time, but only for a limited period of time. The longer you drive with this code, the more likely you are to suffer engine damage if it is due to lean air/fuel ratios.
If you want to avoid damage to your emissions system and catalytic converter, you need to fix this code as soon as possible.
Notes:
An oxygen sensor fault has been detected on Bank 1 as indicated by the P0137 code. There was a low voltage for at least two minutes on the oxygen sensor, which resulted in the code being set. It is the ECM’s responsibility to read the voltage and set the code.
Bank 1 sensor 2 is used to provide voltage feedback to the ECM so the engine can control the fuel-to-air ratio better by measuring the amount of oxygen in the exhaust stream. There is too much oxygen in the exhaust or there are problems that are causing the low voltage condition.
Near the rear of the catalytic converter, Bank 1 Sensor 2 can be found. The catalytic converters’ oxygen capacity is displayed by this signal. For it to work properly, it must maintain a significant amount of voltage, although it isn’t as active as the front sensor.
There are a few other codes very similar to P0137 like P0141 and P0135
Final Words
This guide can be used as a reference to confirm your findings if you suspect that a vehicle is exhibiting symptoms that are consistent with the P0137 code.
In spite of the fact that this trouble code won’t result in the vehicle being unusable, it may result in further damage to certain engine components, which will lead to more expensive and frequent repairs in the future.




