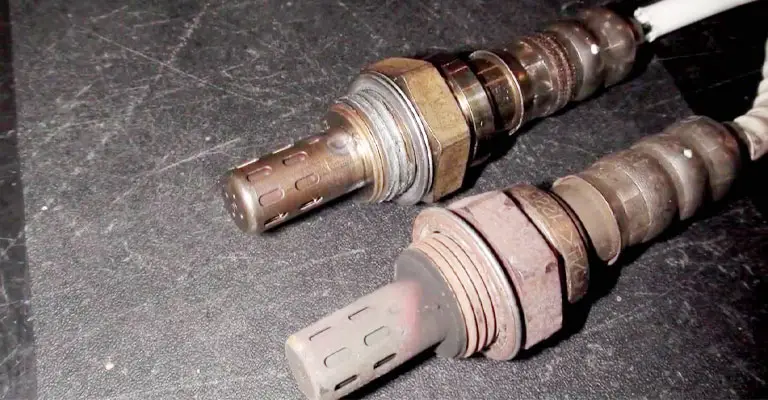
Emissions and pollution from vehicles are reduced by catalytic converters. For example, an engine exhaust catalyst converts harmful emissions into non-harmful gasses by using a platinum and palladium mixture.
Unfortunately, clogged catalytic converters can hurt your engine’s performance, giving you an unsatisfactory ride for no apparent reason. Knowing whether it is clogged or not is, therefore, important.
It is not uncommon for high-mileage vehicles to have a clogged catalytic converter. Usually between 150 and 200 kilometers. This may happen sooner rather than later.
Usually, clogged catalytic converters are caused by something wrong with the vehicle, such as engine misfires or poor fuel quality.
Similarly, the oxygen sensors should be checked when your car isn’t running right, or your check engine light comes on.
Sensors for O2 are usually inexpensive and quick to replace but putting them off or ignoring them altogether can lead to costly and lengthy repairs.
It is difficult to determine if you have a bad catalytic converter or an O2 sensor because the problems are similar.
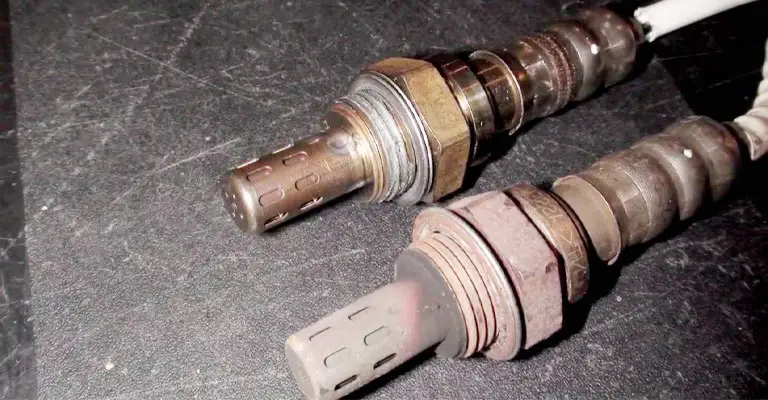

How To Tell If a Catalytic Converter Is Clogged?
The “Check Engine (P0420)” light will usually illuminate when there is a clogged catalytic converter.
There is a lot of money to be spent on catalytic converters, so don’t let your ego get in the way. You can tell if your catalytic converter is clogged if you see these symptoms and signs below:
1. Check Engine Light
Clogged catalytic converters often cause the check engine light to illuminate. However, O2 sensors measure efficiency over a longer period of time, so they report slower than other sensors.
Check engine lights can come on for a variety of reasons, such as engine misfires before they appear for clogged catalytic converters.
Typically, a catalytic converter is to blame if you receive “P0420,” which signifies “Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold.”.
2. Problems With The Engine

It may be difficult to start the engine, have rpm instability, have capped speed, or have poor acceleration. Consequently, the engine is choked because the catalytic converter does not remove the exhaust gasses fast enough.
Temperature gauges tend to run a little hotter when exhaust gasses remain in the engine for too long, causing it to run hotter. There is a limit to the speed at which the car can go, and it won’t go any further.
The backpressure or OBD2 voltage should be checked first, as many other car problems can cause all those symptoms.
3. O2 Voltage/Back Pressure High
OBD2 scanners or exhaust back pressure gauges are the best tools for detecting clogged catalytic converters.
You should be able to find the voltage with an OBD2 scanner in the range of 0.5-0.7V, and there shouldn’t be many fluctuations in it.
Backpressure should be around 1.5 PSI when using an exhaust back pressure gauge. Using a back pressure gauge for catalytic converters, you can easily tell whether the converter is clogged.
You’ll also need to check the back pressure behind the catalytic converter if you have had high back pressure before. You have a clogged muffler if there is still high pressure behind the catalytic converter.
It occurs when pieces of debris break off from a clogged catalytic converter and end up in the exhaust system. Both the catalytic converter and muffler may need to be cleaned/replaced in such a case.
The Signs Of A Bad Oxygen Sensor
In addition to being relatively inexpensive, oxygen sensors can help prevent more expensive problems.
As a result, the computer in your vehicle can adjust the ratio between air and gasoline in its engine if necessary.
Air temperature, altitude, barometric pressure, engine temperature, load on the engine, and more determine the amount of oxygen in an engine.
When too much fuel is left over after combustion, it is referred to as a rich mixture. Nitrogen oxide is more polluting when the mixture is lean without enough fuel. Your oxygen sensor might malfunction if you notice any of these symptoms.
1. Failed Emissions Test

The most common cause of emissions test failures is a bad oxygen sensor. It could cost thousands of dollars to get your vehicle working again if you don’t replace a bad sensor promptly.
In addition, it’s possible that you’ll notice a bad smell in your vehicle, such as rotten eggs. In addition to exposing you and your family to oxygen, a faulty oxygen sensor could also expose you to carbon monoxide.
2. Rough-Sounding Engines
Your vehicle can run irregularly or sound rough when it idles if it has a bad oxygen sensor.
The timing, combustion intervals, and other essential functions of your engine can be affected by a faulty oxygen sensor. There may also be stalling or slow acceleration.
3. Gas Mileage Is Poor
The oxygen sensor in your vehicle could malfunction if you’re spending more on fuel than usual. Oxygen-to-fuel ratios that are too rich or too lean reduce the efficiency of engines.
Also, as oxygen sensors age, their effectiveness decreases, so you’ll probably notice an increase in costs more gradually than suddenly.
4. Check Engine Light On
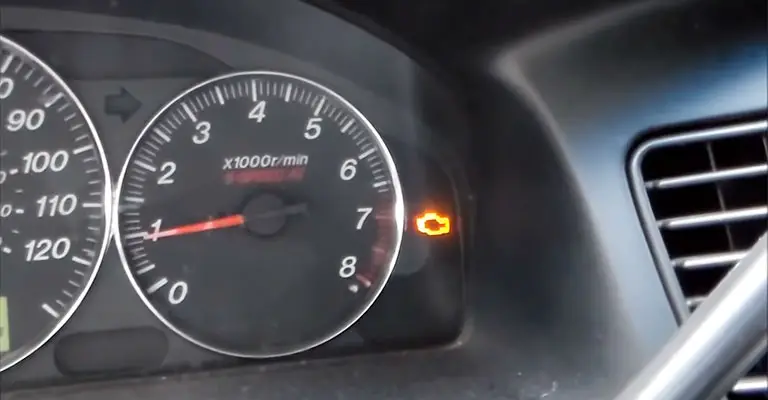

An oxygen sensor that is malfunctioning will normally cause your dashboard’s Check Engine light to glow orange.
You may also have a loose gas cap or another engine problem if your Check Engine light is on. If you are not sure what the problem is with your vehicle, you should have it checked by a professional.
Can A Clogged Catalytic Converter Possibly Cause A Check Engine Light To Come On?
A clogged catalytic converter will cause the check engine light to illuminate. Your catalytic converter is likely clogged if you connect a scanner device, such as the OBD2, and it displays “P0420”.
However, you should remember that the P0420 code will appear if your catalytic converter only loses around 5% of its efficiency, which isn’t much but is still worth addressing.
How Does A Clogged Catalytic Converter Look?
It is possible to see a honeycomb-like structure in catalytic converters if you shine a light through them. You may see debris or feel the flashlight is not as bright as it should be through the other end; if the flashlight isn’t as bright as it should be
What If Your Catalytic Converter Is Clogged? Can You Still Drive?
You can drive your car with a clogged catalytic converter without causing much damage. However, the engine may have problems starting, rpm instability, capped speed, and poor acceleration. Your drive will become unfeasible as a result.
How Do Oxygen Sensors Work?
Sensors play an important role in monitoring fuel consumption, delivery, MPG, timing, and emissions. For example, an engine’s computer analyzes the oxygen in your exhaust pipe by measuring its amount and quality compared to exterior oxygen.
Is It Necessary To Replace All O2 Sensors At Once?
It’s not mandatory, but it’s highly recommended. What’s the reason? All your sensors can be replaced in one appointment to save you time, money, and inconvenience.
In most cases, if you replace just one that has failed, you will be back within three months to replace the other. Labor costs are also incurred as a result of this procedure.
What Is The Number Of Oxygen Sensors In My Vehicle?
The number will vary from vehicle to vehicle, but here is a quick trick to determine how many you have. Your vehicle’s exhaust pipe has one catalytic converter (which converts harmful gasses into less harmful ones).
Therefore, you will have two oxygen sensors per catalytic converter. Many vehicles only have one catalytic converter, so they only have two oxygen sensors, but some have four or more oxygen sensors.
O2 Sensor Replacement Cost
If you have a professional mechanic replace your oxygen sensor, the cost is estimated based on your vehicle’s year, make, and model. Oxygen sensors cost between $30 and $300 brand new.
While hourly labor rates range from $40 to $200, they may still vary based on how many sensors need to be replaced, how difficult it is to gain access to these emission units, and where you bring your vehicle for auto repair.
Note From The Author
Your vehicle could potentially suffer further damage if your catalytic converter quits on you if you ignore the signs of a problem with the O2 sensor.
The cost of a service that used to cost a couple of hundred dollars could now be $500-$2,000 more depending on how many oxygen sensors your vehicle has.
In the same way that O2 sensors are part of a vehicle’s emissions system, catalytic converters are also a part of it.
By alternating rich and lean mixtures, they reduce toxic gasses released into the atmosphere by controlling the amount of air in the exhaust.
However, to function properly, it relies heavily on O2 sensors, even though it is a major part of a car’s emissions system.
A malfunctioning O2 sensor can result in the PCM sending incorrect readings to the catalytic converter, which can cause complete failure.
The Bottom Line
The decision to replace your O2 sensor is ultimately yours once you’ve determined that it is the solution to your problem.
You should, however, keep in mind that determining the cause of an O2 sensor issue is not always straightforward. It’s also possible that you’ll have to replace all of them if the check engine light doesn’t specify.





