Diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) provide information about what your car’s engine is experiencing. You can diagnose the problem yourself if you have an OBD-II code reader and are familiar with the codes.
A three-way catalytic converter (bank 2) problem is the cause of the P0430 engine code on your Honda. It does not pose any immediate danger but may result in a lack of power or poor acceleration if left unattended. To minimize potential damages and repair costs, any repairs should be carried out as soon as possible.
P0430 Definition: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 2)
During the combustion cycle of your vehicle, the catalytic converter converts harmful pollutants into less harmful gases by breaking them down.
Consequently, the vehicle will emit more harmful pollutants due to a malfunctioning catalytic converter.
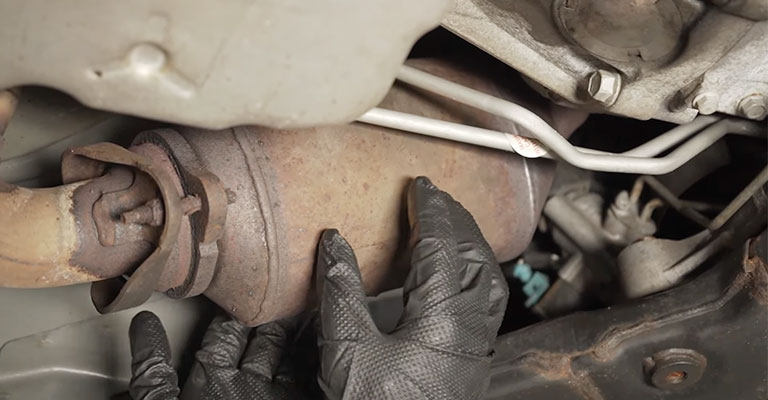

P0430 Engine Code: What Does It Mean?
Your car’s catalyst converter (bank 2) is malfunctioning if you receive the P0430 engine code. The combustion cycle converts harmful pollutants into less harmful gasses by breaking them down.
In the absence of a functioning catalytic converter, less pollutants in the exhaust are broken down, which in turn results in lower oxygen levels (O2).

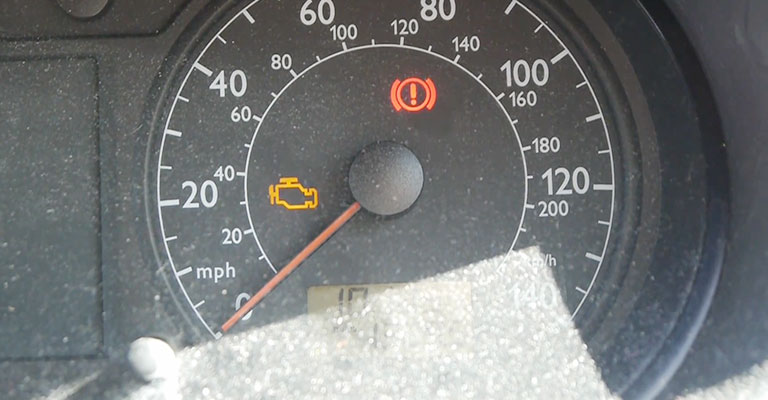
The downstream oxygen sensor informs the vehicle’s computer upon detecting a change in oxygen levels. This causes the computer to activate the check engine light and log the P0430 code.
What Happens When Your Honda Gives You a P0430 Code?
You notice that your vehicle is emitting smoke. Engine stalls, loses power, and idles rough. The check engine light finally illuminates.
You should take your vehicle to an auto repair shop for a thorough checkup and repair if the OBD-II code reader displays the P0430 or P0420 trouble codes.
Most inefficient catalytic converters will not affect the performance of a vehicle. In the event of internal obstruction in the converter, poor engine performance can result, and the engine may even be damaged in the long run.

Before exhaust clogging becomes a problem, the check engine light (MIL) will typically illuminate, so check it out immediately.
While many states do not require vehicle emissions testing, both scenarios can result in higher levels of pollution that may violate state and federal limits.
P0430 Engine Code: What Can Cause It?
In this case, the catalyst system efficiency is below the threshold, thus the P0430 code. Malfunctioning catalytic converters most likely trigger P0430 codes, but oxygen sensors can also be the culprit.
Before being released into the atmosphere, the catalytic converter converts harmful pollutants into less harmful gasses. Oxygen sensors then ensure filtration system integrity. This engine code could also be caused by:

- Having a dirty air filter
- The engine control module (ECM) is faulty
- Timing of the ignition is incorrect
- Spark plugs that are faulty
- Fuel injector(s) leaking
- One or more fuel injectors are faulty
- Oxygen sensor malfunction
- Leaks in the intake air
- Problems with exhaust tubes
Symptoms Of The P0430 Engine Code
A malfunctioning catalytic converter may not result in any symptoms other than an illuminated check engine light. Watch out for the following signs as well:
- It is possible for the Check Engine Light on the dashboard to flash due to catalytic codes.
- A slight lack of power and a dipping idle may be present on the vehicle.
- There is a sulfur or rotten egg smell
- Fuel efficiency has been reduced
- Lack of power in the engine

Diagnosing The P0430 Code
When diagnosing the P0430 code, it is important to complete the entire diagnostic process. For example, an engine misfire or a rich/lean air-fuel ratio can trigger this DTC. It can also be caused by a faulty catalytic converter or oxygen sensor.
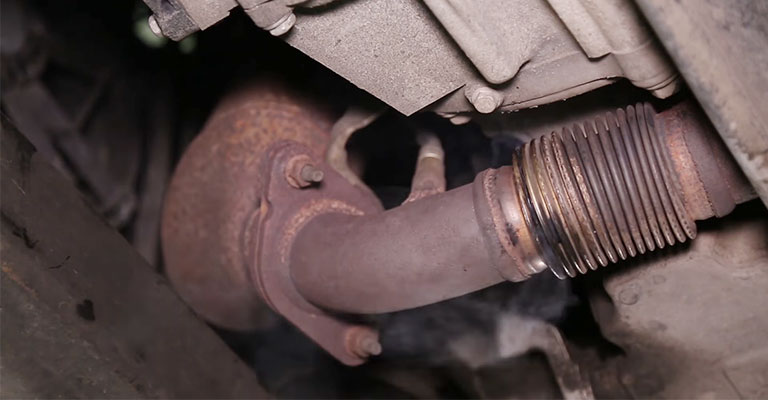

Mistakes To Avoid When Diagnosing P0430
Most commonly, this code is caused by a faulty catalytic converter, but it can also be caused by a faulty O2 sensor or A/F sensor. In addition, there are other codes paired with P0420 that should not be overlooked.
A misfire diagnosis is required for codes like P0300, P0301, P0302, P0303, P03304, P0305, P0306, P0307, and P0308. A new catalytic converter will go bad if the misfire is not repaired before it is replaced.

It is also important to ensure that you do not have any codes P0174, P0171, P0172, or P0175, indicating that your engine is running rich or lean, which can lead to the catalytic converter burning out. So again, it is important to address any codes present, whether they are these codes or other codes.
How Much Will It Cost To Fix Honda Engine Code P0430?
To diagnose the P0430, you will need to spend between $75 and $150 and take about an hour of labor. There is no set cost for repairs, but parts and labor can total anywhere from $100 to $2,400, depending on what needs to be replaced.
A repair of one or more of the following may be required to resolve the underlying issue associated with the P0430 code. Various types of repairs are estimated based on the costs of relevant parts and labor for each repair.
- Repairing an exhaust leak costs $100-$200 (if it has to be welded).
- The cost of a catalytic converter ranges from $400 to $2400
- The price of oxygen or air fuel sensor ranges from $200 to $300
What Is The Seriousness Of The P0430 Engine Code?
There will be no immediate danger to the driver, but the P0430 engine code will cause poor acceleration and decrease engine power. In the event that this component is not repaired, other parts of your car may be severely damaged, necessitating expensive repairs.
The best thing to do is to have your car serviced as soon as possible, even if you feel inconvenient about it. It is difficult or even impossible to diagnose a P0430 if we don’t have the right tools. P0430 codes can be caused by a variety of systems and components.
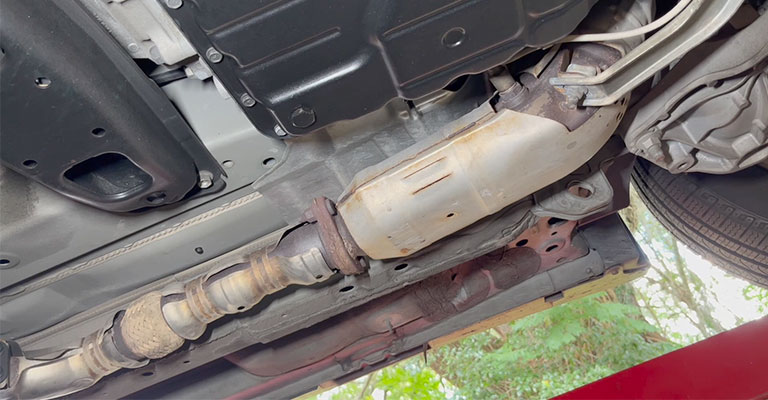

To view misfires, oxygen sensor readings, and live data, technicians need an advanced-level scan tool. By doing so, one can make an accurate diagnosis and avoid costly repairs that aren’t necessary.
Notes About P0430
The oxygen sensors are often mistakenly assumed to be the source of P0430 trouble codes, resulting in immediate replacement of the devices without checking for other possible causes.
Simply replacing the O2 sensors isn’t a worthwhile investment since the problem is usually not the O2 but rather the catalytic converter or another exhaust component.

A P0430 error code can be fixed by vehicle owners with extensive DIY auto repair experience. In any case, it’s best to have the vehicle serviced at a shop to diagnose and fix the problem.
P0430 vs. P0420
There is a mirror image of P0430 and P0420, and it applies to bank 1 converters. It is simply the opposite side of the engine that is referred to as bank 1 and bank 2.
Moreover, straight-cylinder engines have only one bank; some inline six-cylinder engines have two “banks” and two catalytic converters with four O2 sensors. This is the usual configuration for Jeep 4.0L inline six-cylinder engines.

It never hurts to double-check for issues that may lead to catalytic converter problems, even if the OBD-II scanner can distinguish between P0420 and P0430 codes.
Final Words
Several factors can cause the P0430 code, from a faulty oxygen sensor to a faulty catalytic converter. Additionally, each vehicle is unique. Therefore, the factory repair information for your application should be consulted when troubleshooting and repairing DTCs.