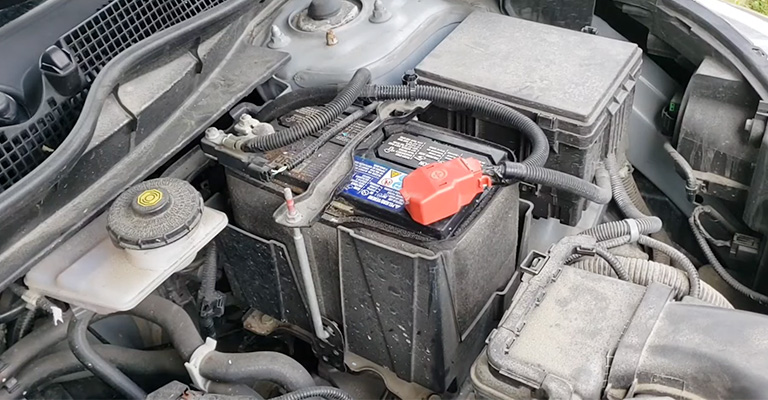
You might have just changed the alternator on your car, and now it won’t start. What do you do? Alternators are the electrical generators on your car that keep the battery charged and provided power to the car’s electrical system.
If your alternator is not working, then you won’t be able to start your car. The first thing to do is to check if the battery is charged. If it isn’t, charge the battery before changing anything else.
Check the battery’s ability to hold a charge and charge it properly before reinstalling. Do not replace anything else until you’ve found the problem.
If the battery doesn’t come back to life, you’ve found it. Before moving on, make sure your battery is fully charged.
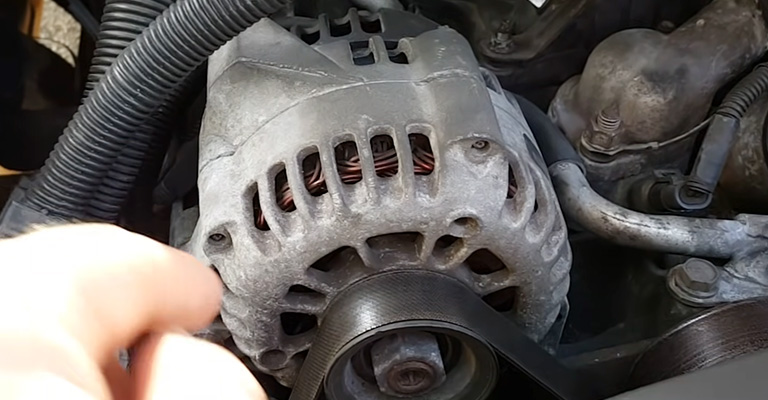

If that doesn’t work, you need to check if the alternator is working properly by checking for a voltage reading from the alternator cable. Again, if it’s not working, replace it with a new one.
If you have a spare battery, you can disconnect the cables from the old one and hook them up to the new one. The last thing you want to do is leave your car sitting for too long with no power because it will drain the battery and ruin it.
Why Won’t My Car Start After Replacing The Alternator?
After replacing your alternator, your vehicle may not start for various reasons. Car owners need to check the battery after replacing an alternator. It is important to check the battery regularly.
It will kill the alternator again if the battery isn’t fully charged. Charging a dead battery with a new alternator is not a good idea.
If you can’t crank the engine over, there may be a problem with the battery, starter, or wiring.
During engine operation, the alternator runs the electrical system, not the starter. While most of these problems don’t require any mechanical or electrical knowledge, others may require some.
1. Loose Connections
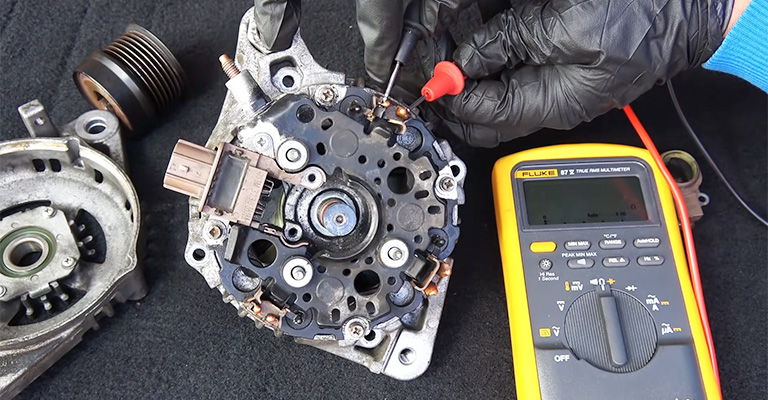
Wires will need to be disconnected when you install new car parts. Unfortunately, one or two may slip through despite being careful when reconnecting them.
It is important to check the battery first. This can happen if the battery is low enough. Next, it is important to check the charging system fuses to see if the battery is fine.
This will occur if one of the alternator wires is shorted during the replacement. It’s possible that something was shorted during the alternator replacement if this occurred right after it was replaced.
Ensure all connections are secure and reconnect some of the wires you previously removed. We tend to overlook the simple things sometimes. Reinstalling parts requires double-checking everything, so it’s a good habit to do so.
2. Corrosion
Batteries can be prevented from delivering electricity by corrosion, but wires can also be eaten by corrosion.
To keep your car in good working order, corrosion must be prevented since it can affect vital components that could put you and your passengers in danger.
Your car’s battery is one place that can have corrosion that prevents it from starting. You connect wires to a car battery’s metal post to power your car’s components. In this case, corrosion will begin once acid hits the metal post.
Make sure the battery wires are disconnected when cleaning off corrosion. To remove corrosion, you will need to use water. For this reason, batteries shouldn’t have any wires connected to them when being cleaned.
Corrosion is impossible to remove once it starts completely, so keeping it at bay is your best bet. It is essential to monitor the corrosion condition regularly.
3. Dead Battery

When you have to change your alternator, a dead battery is a common problem. If your battery is dead, it may be because your alternator failed to charge it.
The battery in your vehicle is one component that relies on the alternator. As your car runs, the alternator provides power to the battery to prevent it from losing charge.
You can resolve this problem by charging the battery at a mechanic shop or auto parts store or idling your vehicle after a jumpstart. Then, the battery can be removed, and the vehicle can be jumpstarted and recharged by a mechanic.
After a jumpstart, your vehicle should run fine since you have installed a new alternator. However, if your car’s alternator hasn’t fully charged your battery yet, you shouldn’t shut it off until you are at the charging location.
A completely dead battery could also be the cause. Your car could have a problem if it won’t start, and no power is present. The date your battery was installed should be on it; it should tell you what year and month it was installed.
If your battery has exceeded four years, you should replace it. Batteries have an expiration date of around four years.
You may not need to replace your battery if you have already had it checked or replaced a new one, and your vehicle won’t start.
4. Faulty Fuel Pump
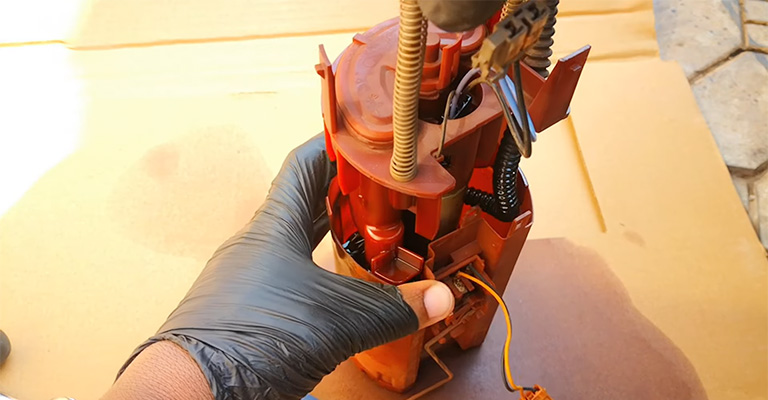
Besides the alternator and battery, there may have been other components that failed simultaneously. Fuel shortage is another possible reason why your vehicle won’t start.
Fuel pumps deliver fuel to engines in cars. If your car does not start, there may be a few problems with the fuel pump.
Having a clogged filter is one of these issues. A fuel pump filter keeps dirt out of your engine by preventing it from getting into the fuel pump. If your filter clogs up, your engine’s pump will have trouble supplying fuel to it.
5. Faulty Unit
Your alternator may have been replaced with a new one, but there is still a chance that it may be defective. The chances of a faulty unit breaking even when new is the same for all components. This is why a warranty should be provided to help solve this problem.
The auto shop where you had your alternator installed is the best place to contact if it malfunctions after being installed. It depends on the store or unit’s warranty policy if car components have a warranty.
If the component you bought from the store or mechanic breaks within a certain time, you should ask for a replacement. For example, an alternator or battery problem is usually at the root of a vehicle’s inability to start.
6. Tuning
Have you disconnected the battery? In this case, the computer in the car will dump its learned fuel strategy and ignition curve data.
If you have a new PCM or have reset it, the engine will run using a pre-programmed strategy until the engine is tuned on its own as it runs. The symptoms may not be obvious, or the engine might not run properly until it’s run for a while.
While the amount of time it takes depends on the car, generally running the car for 30 minutes (as long as the Check Engine Light isn’t on) while varying speeds gives the PCM enough time to tune itself.
You will need to investigate whether a wire or vacuum line was misplaced, misconnected, or damaged when the alternator was replaced if the check engine light is on or hasn’t resolved itself after a little while.
Troubleshooting
Sometimes these things happen, and it’s best to diagnose them and figure out what went wrong. But then, it’s time to get started!
Test The Battery:

Your car battery needs to have a good voltage between 12.6 volts and 14.5 volts. This is because it cannot be jumped without reconditioning or replaced if it is too drained.
Check Your Connections:
Have you checked that everything is set up correctly? Make sure you got everything during installation by reviewing and retracing your steps.
Test The New Alternator:
There are times when even brand-new parts fail. To ensure the new alternator works properly, pull out your handy-dandy multimeter and test it.
Check Other Parts:
Among other components, you may have a problem with your fuel pump, oil pump, starter, transmission, or starter motor.
If you cannot find the problem, you might need to visit a mechanic who can diagnose it with better tools than most DIY repair car owners.
Do I Need A New Battery After Replacing The Alternator?
Changing the alternator does not require replacing the battery. Therefore, despite these two components working together, if one breaks, the other one should not be affected as well.
Your battery will get drained whenever your alternator fails, which is the most common problem you will encounter.
It is not necessary to replace the battery if this happens but to recharge it again. The battery has a typical lifespan of four years, so if your alternator is over four years old, it’s also a good idea to replace it.
How Many Years Does An Alternator Last?
You should know when your car’s alternator needs replacing again after it has been replaced. A typical alternator lasts between 85,000 and 100,000 miles or 7 to 10 years.
It is also possible to decrease the life of your alternator by using aftermarket parts. To extend the life of your alternator’s life, you must use OEM auto parts whenever you replace components.
The alternator will also need more power if you drive on steep roads or push your vehicle a lot. It is a good idea to regularly inspect your components because you may find signs that can aid in preventing their failure.
Note:
Prior to condemning the starter, make sure the battery is appropriately charged. Boost packs work in different ways. Jumping a completely discharged battery won’t work, especially if a malfunctioning alternator has likely abused the battery.
The battery is probably dead now. If the battery isn’t functioning properly, take it back to one of those stores, have them test it again, and perhaps recheck the alternator.
Final Words
Bad connections are often the cause of intermittent electrical problems. The problem has yet to be fixed over the years, even after people have spent $ 100’s on replacing parts.
The two battery terminals should be checked for all small wires. Instead of just looking at them, take all the wires off the terminals, sand them, and scrape them clean.
You may need to replace any connectors if necessary. The chassis ground connection should also be checked at the other end of the small wires.




